# Sentinel源码分析-Sentinel滑动时间窗口算法源码解析
上节课我们分析了Sentinel的滑动时间窗口算法原理,那么这节课我们来研究一下源码中的具体实现
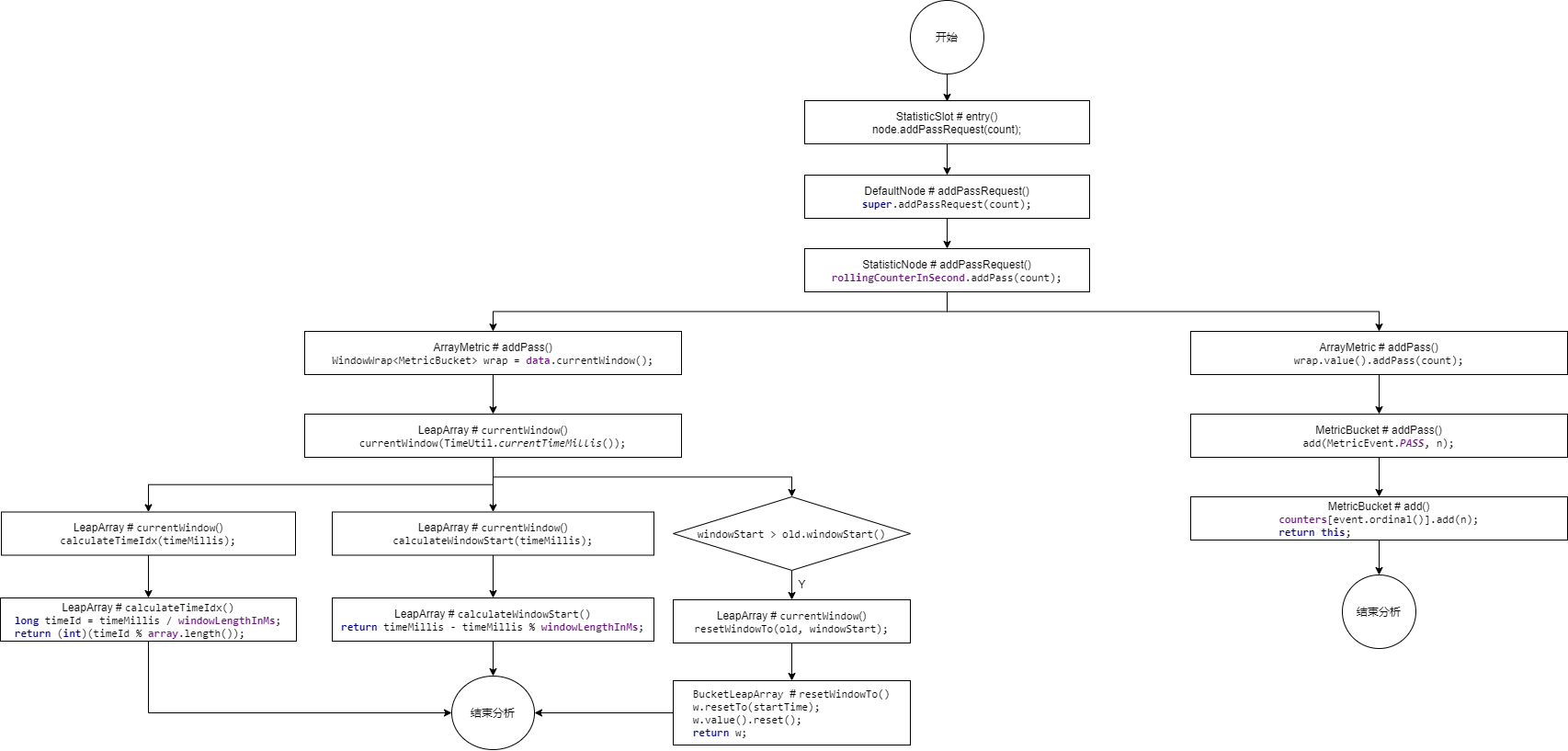
# 整体流程图
# 源码分析
那我们就按照这个流程图来从头分析
首先看StatisticSlot.entry方法中node.addPassRequest(count)方法,这里我之前就提到过用到了滑动窗口算法,那我们来具体分析
// 增加通过请求的数量(这里涉及到滑动窗口算法)
node.addPassRequest(count);
1
2
2
进入方法DefaultNode.addPassRequest
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {
super.addPassRequest(count);
this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
继续向下跟踪
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {
// 为滑动计数器增加本次的访问数据
rollingCounterInSecond.addPass(count);
rollingCounterInMinute.addPass(count);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
最后进入ArrayMetric.addPass,这是一个使用数组保存数据的计量器类
@Override
public void addPass(int count) {
// 获取当前时间点所在的样本窗口
WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow();
// 将当前请求的计数量添加到当前样本窗口的统计数据中
wrap.value().addPass(count);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
先来跟踪data.currentWindow();
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow() {
// 获取当前时间所在的样本窗口
return currentWindow(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis());
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
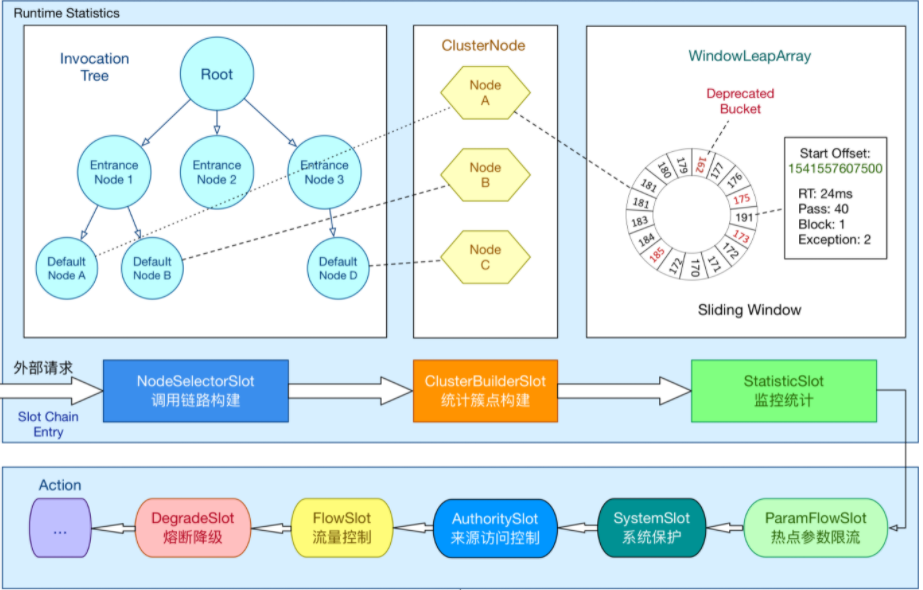
这里就会进入LeapArray(环形数组)中的currentWindow方法中,这个环形数组,其实就是Sentinel官方提供的原理图中的环形数组WindowLeapArray
// 环形数组
public abstract class LeapArray<T> {
// 样本窗口长度
protected int windowLengthInMs;
// 一个时间窗中包含的时间窗数量
protected int sampleCount;
// 时间窗长度
protected int intervalInMs;
private double intervalInSecond;
// 这个一个数组,元素为WindowWrap样本窗口
// 注意,这里的泛型 T 实际为 MetricBucket 类型
protected final AtomicReferenceArray<WindowWrap<T>> array;
......
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
这里要注意这个数组,这个数组里面所存放的类型就是WindowWrap窗口类型,泛型T是MetricBucket这里我们来看一下这个类型
public WindowWrap(long windowLengthInMs, long windowStart, T value) {
//样本窗口长度
this.windowLengthInMs = windowLengthInMs;
//样本窗口的起始时间戳
this.windowStart = windowStart;
//当前样本窗口的统计数据 其类型为MetricBucket
this.value = value;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//..LeapArray
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow() {
// 获取当前时间所在的样本窗口
return currentWindow(TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis());
}
//------------------------------------------------------------
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {
if (timeMillis < 0) {
return null;
}
// 计算当前时间所在的样本窗口id,即在计算数组LeapArray中的索引
int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);
// Calculate current bucket start time.
// 计算当前样本窗口的开始时间点
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);
.....
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
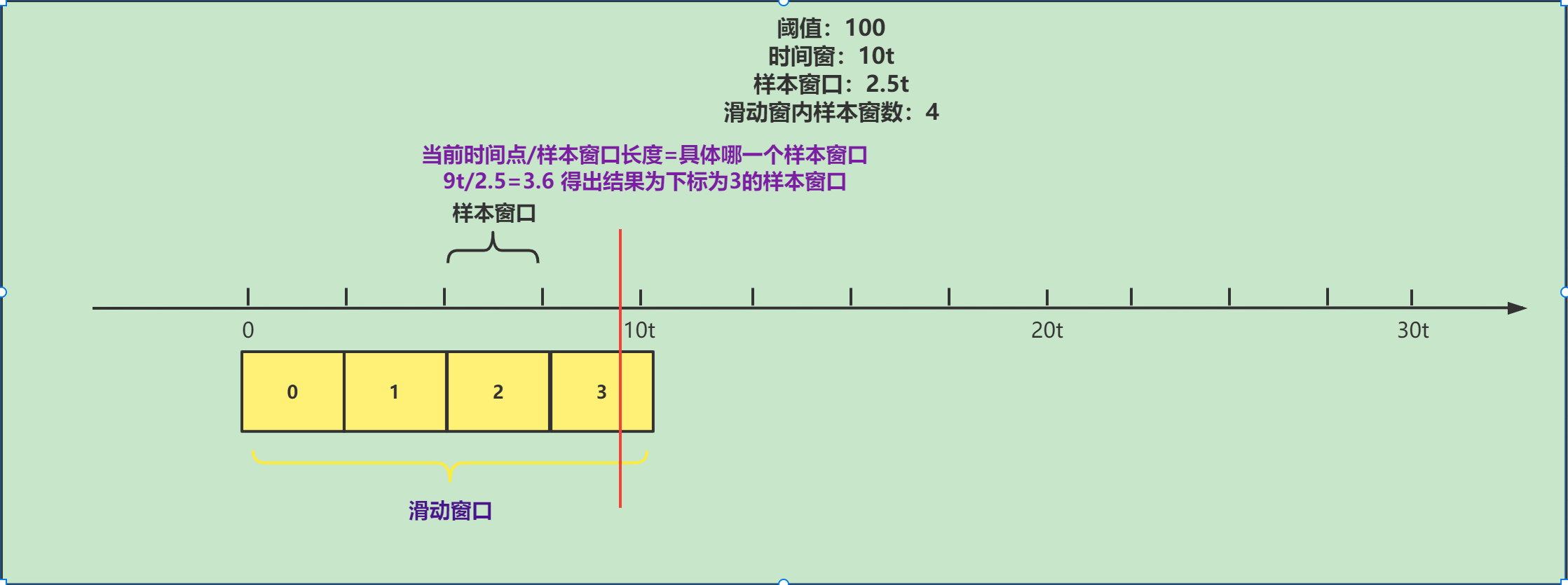
在这里我们先分析calculateTimeIdx方法
private int calculateTimeIdx(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) {
// 计算当前时间在那个样本窗口(样本窗口下标),当前时间/样本窗口长度
long timeId = timeMillis / windowLengthInMs;
// Calculate current index so we can map the timestamp to the leap array.
// 计算具体索引,这个array就是装样本窗口的数组
return (int)(timeId % array.length());
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
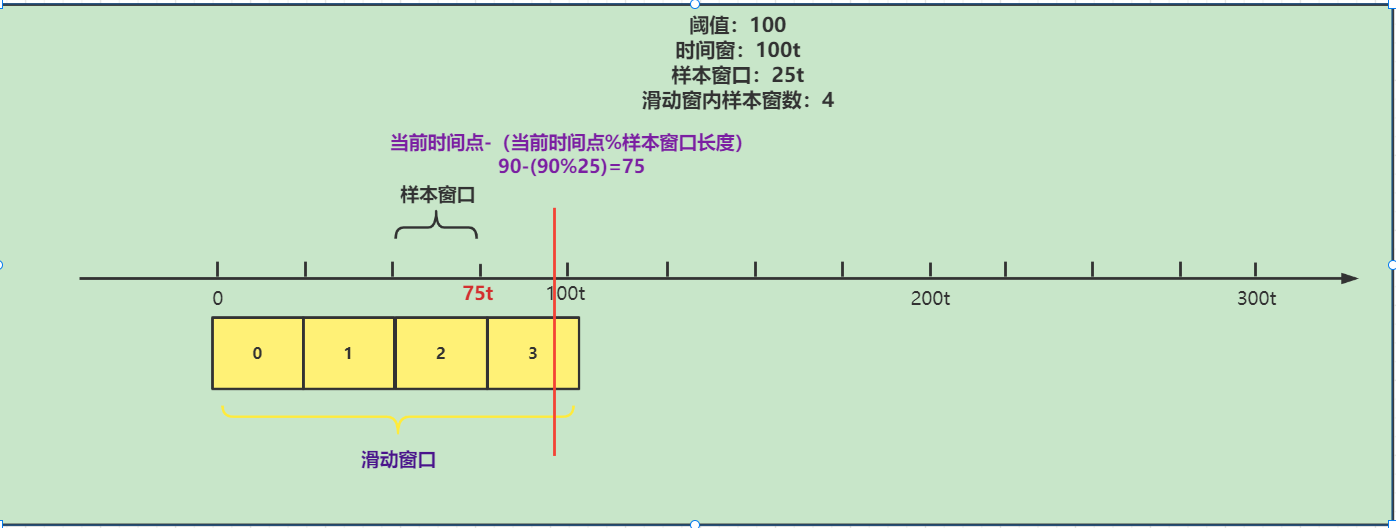
timeId(样本窗口下标)原理如下:
具体索引原理:
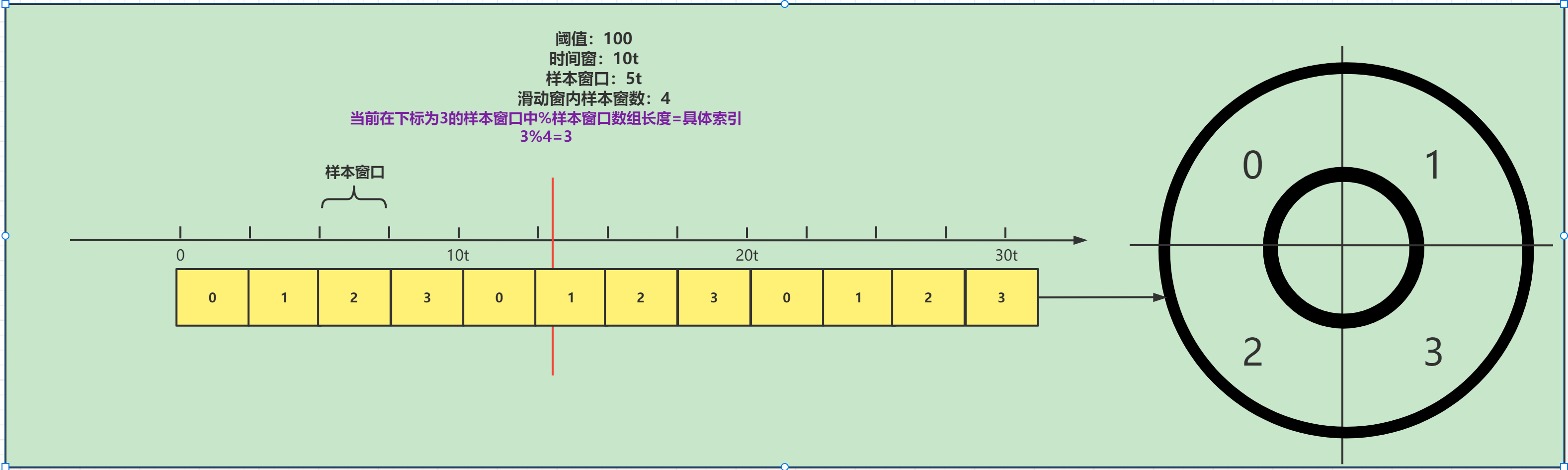
这里分析完成我们接着分析这里,计算当前样本窗口的起点
// 计算当前样本窗口的开始时间点
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);
//------------------------------
protected long calculateWindowStart(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) {
// 计算当前样本窗口的起点 当前时间点-(当前时间点%样本窗口长度)
return timeMillis - timeMillis % windowLengthInMs;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
原理如下:
这里分析完成之后我们继续向下分析
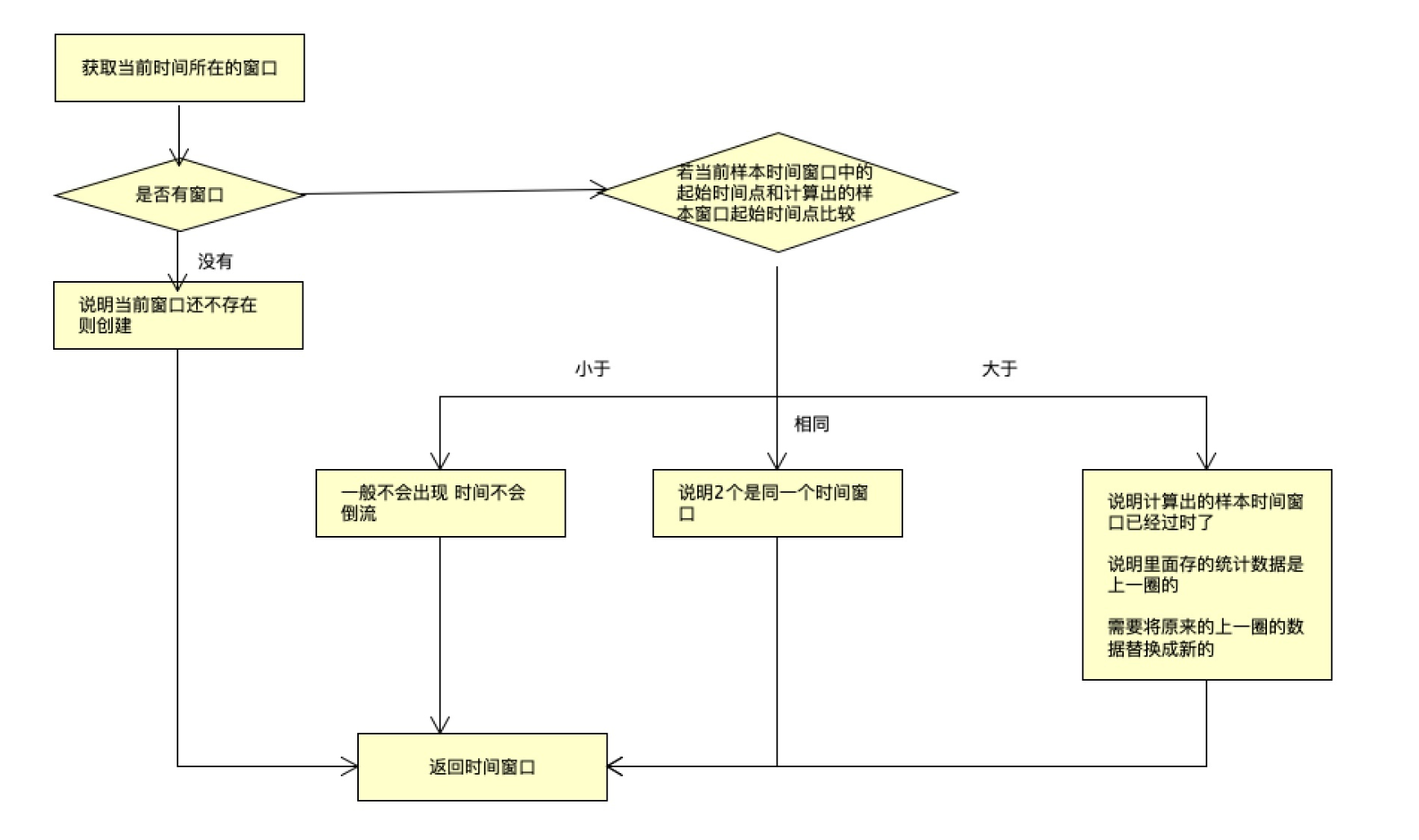
while (true) {
// 获取到当前时间所在的样本窗口
WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);
// 如果获取不到,表示没有创建
if (old == null) {
/*
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
* bucket is empty, so create new and update
*
* If the old bucket is absent, then we create a new bucket at {@code windowStart},
* then try to update circular array via a CAS operation. Only one thread can
* succeed to update, while other threads yield its time slice.
*/
// 创建新的时间窗口
WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
// 通过CAS方式将新建窗口放入Array
if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {
// Successfully updated, return the created bucket.
return window;
} else {
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
// 若当前样本窗口的起始时间点与计算出的样本窗口起始点相同,则说明两个是同一个样本窗口
} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {
/*
* B0 B1 B2 B3 B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
* startTime of Bucket 3: 800, so it's up-to-date
*
* If current {@code windowStart} is equal to the start timestamp of old bucket,
* that means the time is within the bucket, so directly return the bucket.
*/
return old;
// 若当前样本窗口的起始时间点 大于 计算出的样本窗口起始时间点,说明计算出的样本窗口已经过时了,
// 需要将原来的样本窗口替换
} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {
/*
* (old)
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* |_______||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* ... 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 timestamp
* ^
* time=1676
* startTime of Bucket 2: 400, deprecated, should be reset
*
* If the start timestamp of old bucket is behind provided time, that means
* the bucket is deprecated. We have to reset the bucket to current {@code windowStart}.
* Note that the reset and clean-up operations are hard to be atomic,
* so we need a update lock to guarantee the correctness of bucket update.
*
* The update lock is conditional (tiny scope) and will take effect only when
* bucket is deprecated, so in most cases it won't lead to performance loss.
*/
if (updateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// Successfully get the update lock, now we reset the bucket.
// 替换掉老的样本窗口
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);
} finally {
updateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
// 当前样本窗口的起始时间点 小于 计算出的样本窗口起始时间点,
// 这种情况一般不会出现,因为时间不会倒流。除非人为修改了系统时钟
} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {
// Should not go through here, as the provided time is already behind.
return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
这里的原理如下:
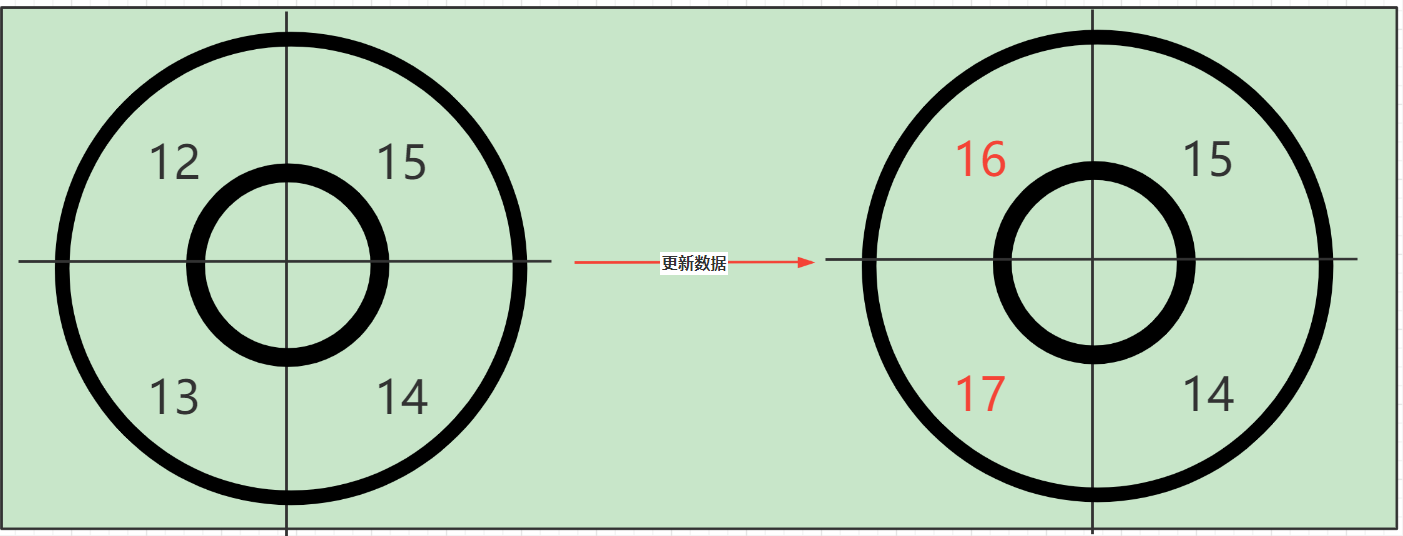
具体是如何替换的拿,我们来看源码
// 替换掉老的样本窗口
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);
//------------------------------------------------------------
// BucketLeapArray.resetWindowTo
@Override
protected WindowWrap<MetricBucket> resetWindowTo(WindowWrap<MetricBucket> w, long startTime) {
// Update the start time and reset value.
// 更新窗口起始时间
w.resetTo(startTime);
// 将多维度统计数据清零
w.value().reset();
return w;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
更新数据分析
public MetricBucket reset() {
// 将每个维度的统计数据清零
for (MetricEvent event : MetricEvent.values()) {
counters[event.ordinal()].reset();
}
initMinRt();
return this;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
最后我们再来看一下具体是那个维度,其实是通过维度
@Override
public void addPass(int count) {
// 获取当前时间点所在的样本窗口
WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow();
// 将当前请求的计数量添加到当前样本窗口的统计数据中
wrap.value().addPass(count);
}
//----------------------------------------
public void addPass(int n) {
add(MetricEvent.PASS, n);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11