# Sentinel源码解析-熔断降级DegradeSlot解析
上节课我们分析完了限流FlowSlot,那么我们继续想下一个链路中的元素来看,下一个就是熔断降级的Slot,那我们直接来看核心方法
//DegradeSlot.entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 熔断降级检测
performChecking(context, resourceWrapper);
// 触发下一个节点
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
那我们先来跟踪熔断降级检测的方法,在这里我们可以看见,这里其实就是对熔断器的状态进行判断
void performChecking(Context context, ResourceWrapper r) throws BlockException {
// 获取所有资源的熔断器
List<CircuitBreaker> circuitBreakers = DegradeRuleManager.getCircuitBreakers(r.getName());
// 判断是否获取到熔断器,如果为空直接结束
if (circuitBreakers == null || circuitBreakers.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (CircuitBreaker cb : circuitBreakers) {
// 判断所有熔断器的状态,如果是开启状态直接抛出异常
if (!cb.tryPass(context)) {
// 此异常继承于BlockException
throw new DegradeException(cb.getRule().getLimitApp(), cb.getRule());
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
而真正判断是否需要开启熔断器是在exit方法中进行的,这个方法是在业务方法执行以后调用了,熔断器需要手机业务异常或者业务的执行时间来判断是开启熔断
@Override
public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper r, int count, Object... args) {
// 如果当前其他的Slot已经有了BlockException,就直接跳过
Entry curEntry = context.getCurEntry();
if (curEntry.getBlockError() != null) {
fireExit(context, r, count, args);
return;
}
// 通过资源名称获取熔断器
List<CircuitBreaker> circuitBreakers = DegradeRuleManager.getCircuitBreakers(r.getName());
if (circuitBreakers == null || circuitBreakers.isEmpty()) {
fireExit(context, r, count, args);
return;
}
if (curEntry.getBlockError() == null) {
// passed request
// 调用CircuitBreaker的onRequestComplete()方法
for (CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker : circuitBreakers) {
circuitBreaker.onRequestComplete(context);
}
}
fireExit(context, r, count, args);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
在这个代码中,有一个比较关键的地方就是CircuitBreaker(熔断器),那我们来分析一下:
# CircuitBreaker熔断器
首先我们要知道其实CircuitBreaker是一个接口
/**
* 熔断器中将三种熔断策略封装(慢调用比例/异常比例/异常数)为两种熔断器:
* 响应时间熔断器、异常熔断器
*/
public interface CircuitBreaker {
/**
* Get the associated circuit breaking rule.
*
* @return associated circuit breaking rule
* 获取熔断规则
*/
DegradeRule getRule();
/**
* Acquires permission of an invocation only if it is available at the time of invoking.
*
* @param context context of current invocation
* @return {@code true} if permission was acquired and {@code false} otherwise
* 判断是否需要降级 返回值为false开启降级
*/
boolean tryPass(Context context);
/**
* Get current state of the circuit breaker.
*
* @return current state of the circuit breaker
* 当前熔断器状态
*/
State currentState();
/**
* <p>Record a completed request with the context and handle state transformation of the circuit breaker.</p>
* <p>Called when a <strong>passed</strong> invocation finished.</p>
*
* @param context context of current invocation
* 回调方法 当请求通过后触发
*/
void onRequestComplete(Context context);
/**
* Circuit breaker state.
* 三种熔断器状态:
* OPEN开启
* HALF_OPEN半开启
* CLOSED关闭
*/
enum State {
/**
* In {@code OPEN} state, all requests will be rejected until the next recovery time point.
*/
OPEN,
/**
* In {@code HALF_OPEN} state, the circuit breaker will allow a "probe" invocation.
* If the invocation is abnormal according to the strategy (e.g. it's slow), the circuit breaker
* will re-transform to the {@code OPEN} state and wait for the next recovery time point;
* otherwise the resource will be regarded as "recovered" and the circuit breaker
* will cease cutting off requests and transform to {@code CLOSED} state.
*/
HALF_OPEN,
/**
* In {@code CLOSED} state, all requests are permitted. When current metric value exceeds the threshold,
* the circuit breaker will transform to {@code OPEN} state.
*/
CLOSED
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
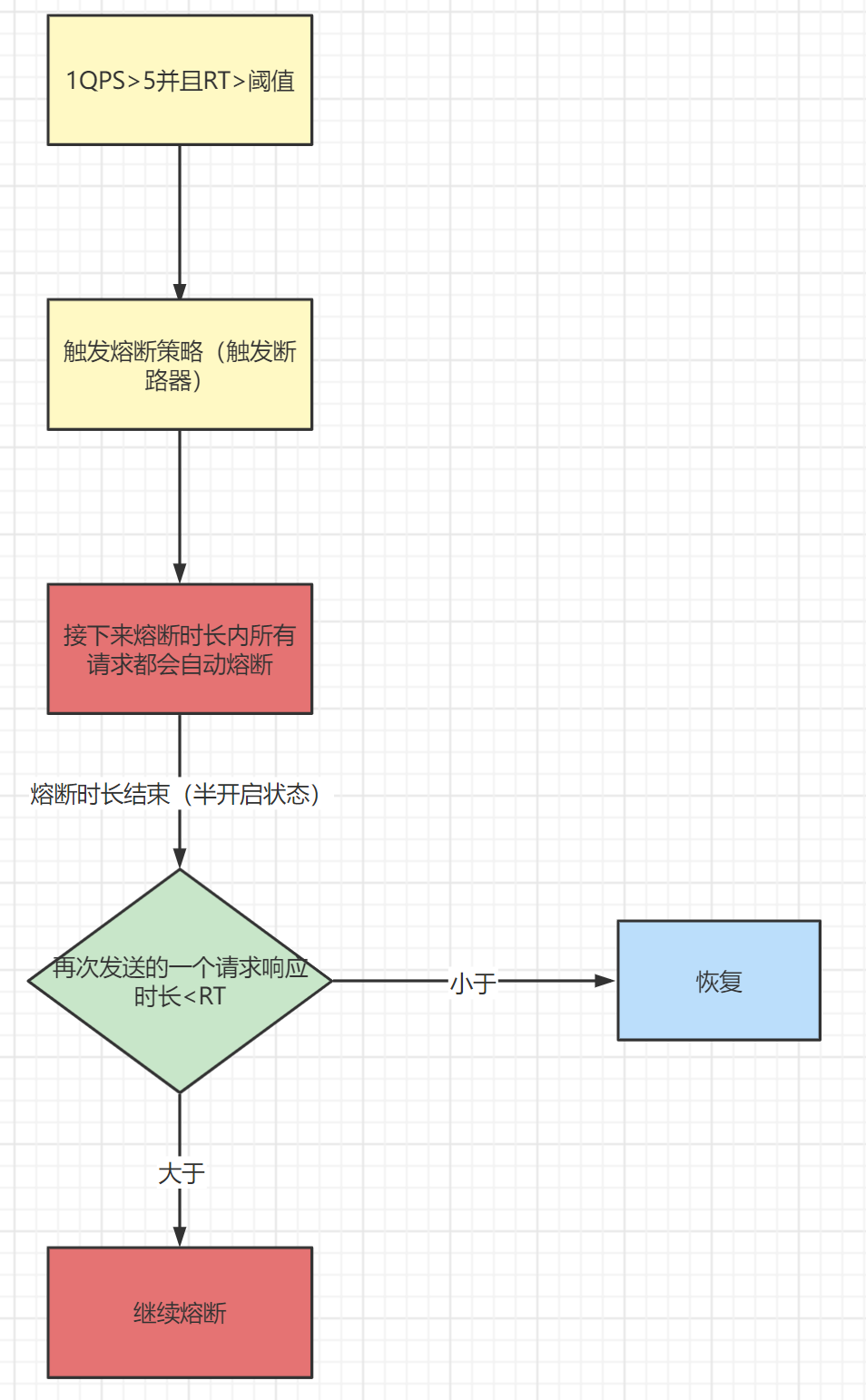
以上代码中其中三种熔断状态对应的原理如下(这个原理在基础应用讲过)
# 熔断策略
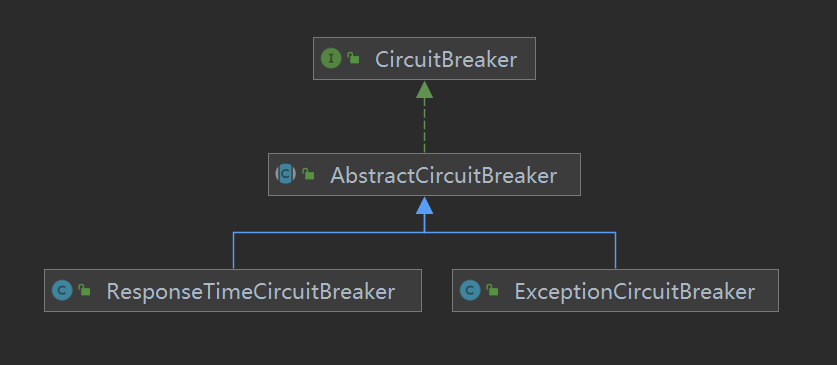
对应的实现类有两个ExceptionCircuitBreaker(异常熔断器)、ResponseTimeCircuitBreaker(响应时间熔断器),这个我们可以从类图看到
那我们这里来看看ExceptionCircuitBreaker(异常熔断器),对应的策略是
我们来看对应回调方法ExceptionCircuitBreaker.onRequestComplete
@Override
public void onRequestComplete(Context context) {
Entry entry = context.getCurEntry();
if (entry == null) {
return;
}
Throwable error = entry.getError();
// 异常事件窗口计数器
SimpleErrorCounter counter = stat.currentWindow().value();
// 如果有异常,异常数+1
if (error != null) {
counter.getErrorCount().add(1);
}
// 总异常数+1
counter.getTotalCount().add(1);
handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(error);
}
private void handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(Throwable error) {
// 如果熔断器已经开启直接返回
if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) {
return;
}
// 进入办开启状态
if (currentState.get() == State.HALF_OPEN) {
// In detecting request
if (error == null) {
// 本次请求没有出现异常,关闭熔断器
fromHalfOpenToClose();
} else {
// 本次请求出现异常,打开熔断
fromHalfOpenToOpen(1.0d);
}
return;
}
List<SimpleErrorCounter> counters = stat.values();
long errCount = 0; //异常数量
long totalCount = 0; //总异常数
for (SimpleErrorCounter counter : counters) {
errCount += counter.errorCount.sum();
totalCount += counter.totalCount.sum();
}
// 请求数量<最小的请求数量时不开启熔断
if (totalCount < minRequestAmount) {
return;
}
double curCount = errCount;
// 熔断策略为慢调用比例
if (strategy == DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO) {
// Use errorRatio
// 计算百分比
curCount = errCount * 1.0d / totalCount;
}
// 错误率或者错误数大于阈值时开启熔断
if (curCount > threshold) {
transformToOpen(curCount);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61